Introduction
In this blog, you'll learn how to build a production-ready, serverless data pipeline on Google Cloud Platform that automatically ingests data from an external API and loads it into BigQuery for analysis.
This is part 2 / 2 of the blog.
Step 6: Create a BigQuery Table

6.1 Create a Dataset
- Navigate to BigQuery
- Click your project name
- Click "Create Dataset"
- Name it `api_data' under data set ID
- Choose same region as your bucket
- Click "Create Dataset"
6.2 Create the Raw Table
Click on your dataset, then "Create Table":
Configuration:
- Source: Empty table
- Table name:
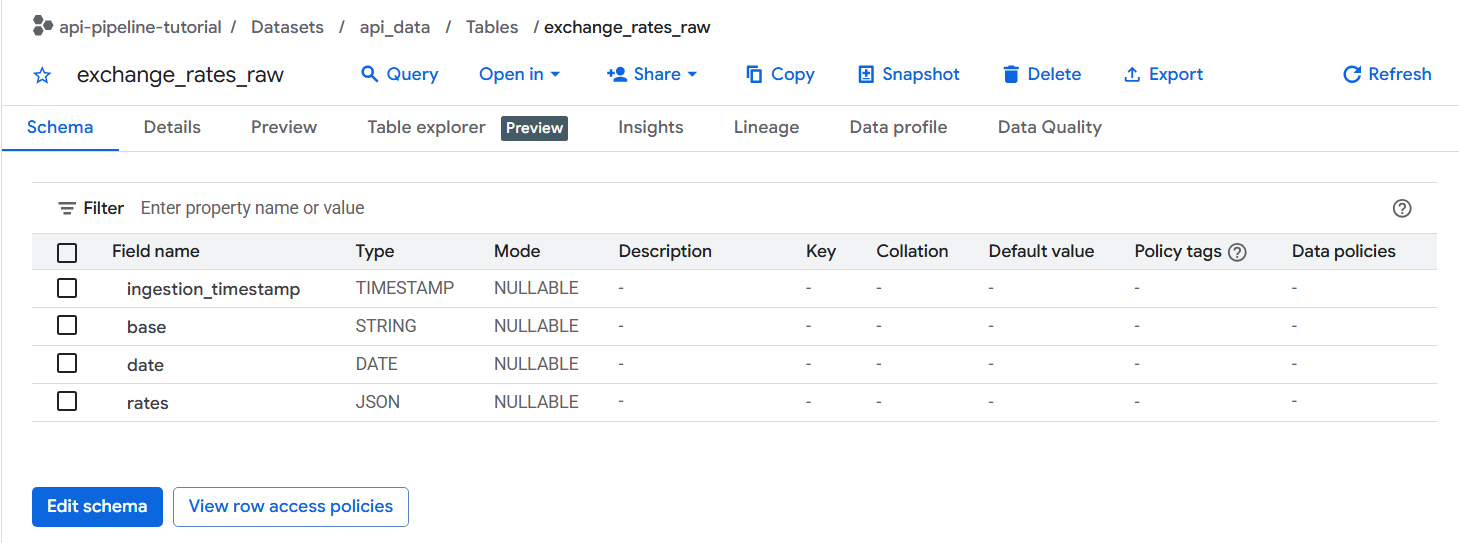
exchange_rates_raw - Schema: Add these fields manually
ingestion_timestamp TIMESTAMP REQUIRED
base STRING REQUIRED
date DATE REQUIRED
rates JSON REQUIRED
6.3 Alternative: Create Table with SQL
Or use this SQL in the BigQuery console:
CREATE TABLE `api_data.exchange_rates_raw` (
ingestion_timestamp TIMESTAMP NOT NULL,
base STRING NOT NULL,
date DATE NOT NULL,
rates JSON NOT NULL
);
Step 7: Load Data into BigQuery
7.1 Schedule the Load Query
Click "Schedule queries" → "Create a scheduled query"
Insert the following below and click "Schedule"
LOAD DATA INTO api-pipeline-tutorial.api_data.exchange_rates_raw (ingestion_timestamp TIMESTAMP, base STRING, date DATE, rates JSON)
FROM FILES (
format = 'JSON',
uris = ['gs://api-pipeline-data/raw/exchange_rates/*.json']
);
- Name:
hourly_data_load - Schedule: 1 every hour
- Destination table: Leave this unticked
- Click "Save"
Step 8: Handle Duplicates (Optional)
8.1 Understanding the Duplicate Problem
Since we're using append-only loads, the same file might be loaded multiple times if it's still in the bucket. This is intentional for raw data!
8.2 Create a Deduplicated View
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW `api_data.exchange_rates_clean` AS
SELECT *
FROM (
SELECT *,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (
PARTITION BY base, date, ingestion_timestamp
ORDER BY ingestion_timestamp DESC
) AS rn
FROM `api_data.exchange_rates_raw`
)
WHERE rn = 1;
8.3 Query the Clean Data
SELECT
ingestion_timestamp,
base,
date,
JSON_EXTRACT(rates, '$.EUR') as EUR_rate
FROM `api_data.exchange_rates_clean`
ORDER BY date DESC, ingestion_timestamp DESC
LIMIT 10;
Step 9: Monitor Your Pipeline
9.1 Check Cloud Scheduler Logs
Navigate to Cloud Scheduler → Click your job → "Logs"
9.2 Check Cloud Function Logs
Navigate to Cloud Functions → Click your function → "Logs"
9.3 Verify Data Freshness
Create a monitoring query:
SELECT
MAX(ingestion_timestamp) as last_ingestion,
TIMESTAMP_DIFF(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(), MAX(ingestion_timestamp), MINUTE) as minutes_since_last_run,
COUNT(*) as total_records
FROM `api_data.exchange_rates_raw`;
Step 10: Test End-to-End
10.1 Force a Complete Run
- Go to Cloud Scheduler
- Click "Force Run" on your job
- Wait 1-2 minutes
- Check Cloud Storage for new file
- Wait for scheduled load (or run manually)
- Query BigQuery for new data
10.2 Verify the Full Pipeline
Run this comprehensive check:
SELECT
DATE(ingestion_timestamp) as ingestion_date,
COUNT(*) as records_per_day,
COUNT(DISTINCT base) as unique_bases,
MIN(ingestion_timestamp) as first_load,
MAX(ingestion_timestamp) as last_load
FROM `api_data.exchange_rates_raw`
GROUP BY DATE(ingestion_timestamp)
ORDER BY ingestion_date DESC;
Summary
Congratulations! 🎉 You've built a production-ready serverless data pipeline on GCP!
What you accomplished:
- ✅ Automated API data ingestion every hour
- ✅ Raw data storage in Cloud Storage
- ✅ Structured data warehouse in BigQuery
- ✅ Scheduled data loading
- ✅ Duplicate handling and data quality
Key skills learned:
- Cloud Functions development and deployment
- Cloud Scheduler configuration
- BigQuery table design and loading patterns
- Data deduplication strategies
- End-to-end pipeline monitoring
Architecture built:
Cloud Scheduler → Cloud Functions → Cloud Storage → BigQuery
(Hourly) (Python API) (JSON Files) (Analytics)
