Using a virtual environment creates a self-contained sandbox for your project, ensuring that the specific libraries and versions you install never conflict with other projects or your global system. This prevents "dependency hell"—where updating a tool for one app accidentally breaks another—and guarantees that your code remains stable and reproducible no matter what else is installed on your computer.
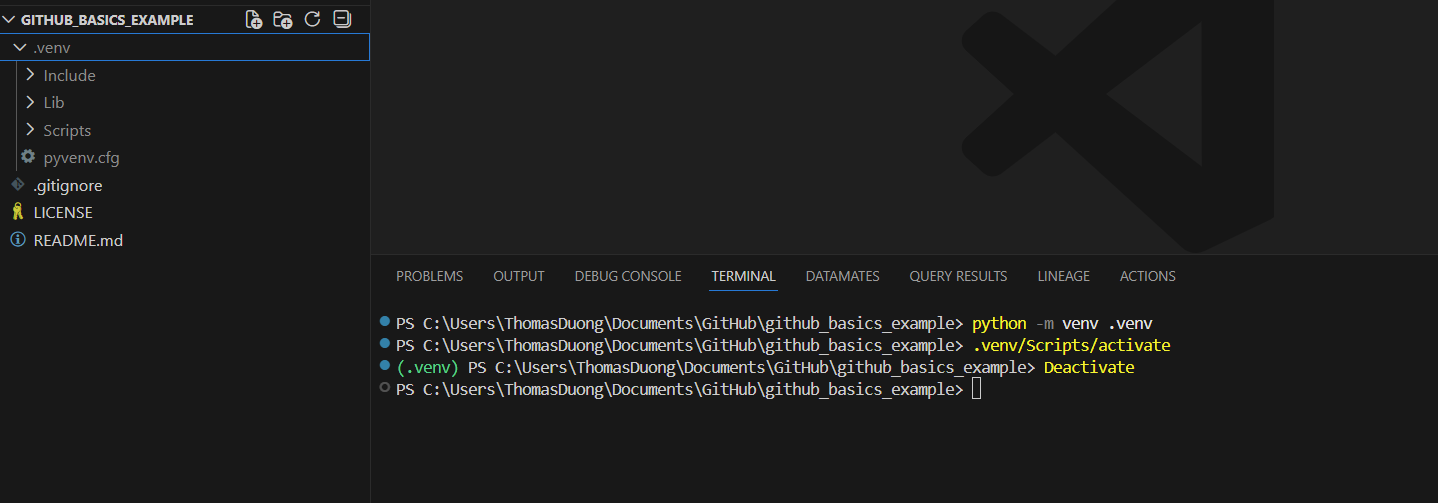
1) Open the Terminal
Go to the top menu bar and select Terminal > New Terminal
2) Create the Virtual Environment
python -m venv .venv
3) Activate the Environment
.venv\Scripts\activate
4) Deactivate the Environment
Deactivate